Summary: A new system that uses ultrafast fMRI is capable to capture mind activity at sub-second amounts. The approach will allow for true-time monitoring of the mind beneath stimulation situations.
Supply: College of Queensland
Brain stimulation, these types of as Deep brain stimulation (DBS), is a strong way to deal with neurological and psychiatric diseases. Though it has offered therapeutic gain for sufferers of Parkinson’s, Alzheimer’s, and habit for additional than a decade, its fundamental neural mechanism is not nevertheless thoroughly comprehended.
Researchers at the Queensland Mind Institute (QBI) are now one step nearer to unravelling the secret of mind action to improved have an understanding of this system and perhaps forecast DBS results.
The brain is a hugely intricate community of circuits organised hierarchically with large-ranging connections. Connections go in distinctive directions, forwards and backwards, and among neurons that are possibly excitatory – the accelerators of a response – or inhibitory – the brakes modifying a reaction.
“Say you want to transfer your hand – as soon as that signal is initiated, we hope that the activity that follows relies upon on the brain’s neural networks,” Associate Professor Kai-Hsiang Chuang said.
“What we don’t fully fully grasp is how or when these structural and purposeful elements of the brain interact to at some point lead to the end result of moving your hand.”
Useful MRI (fMRI) is the most well-liked procedure utilised to analyze brain networks. fMRI tracks blood movement and oxygenation adjustments subsequent neural activity, therefore indirectly measuring the functional connections currently being fashioned, and giving us an indication of where by mind action is propagating.
Brain activity, however, is not as straightforward as a sign travelling from spot to region.
The crew at the Chuang laboratory have created a new ultrafast fMRI strategy with a vastly amplified temporal resolution, enabling them to seize the dynamics of mind exercise at a sub-next amount.
Affiliate Professor Chuang said the new strategy experienced led to far more thorough knowledge of how and when the brain’s structural and practical connections interact.
“The first new discovery we created is that mind exercise not only propagates via structural wiring but follows particular preferential circuits depending on their excitatory and inhibitory neuronal distribution,” he stated.
“Communication in between brain locations of related mobile forms gets to be far more fluent, and the brain exercise stronger.”
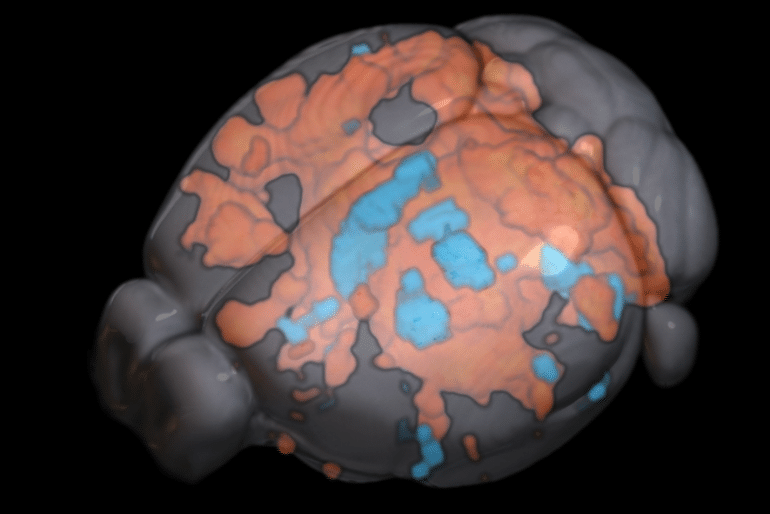
The Chuang team tracked the brain action of mice each even though stimulated and at relaxation working with their ultrafast fMRI procedure. When the brain was stimulated, action adopted the structural wiring in the forward direction — from A to B and then B to C. When the brain was at rest, exercise was a lot more dependent on cell style organisation and less on structural wiring, propagating among C and B but not with A, if that is where the preferential circuit was.
This implies that how details is processed is really dependent on your state, where it was formerly thought that brain action functioned in the exact same way whether at relaxation or occupied carrying out a undertaking.
“The next discovery we created was that the blood sign detected by fMRI could replicate the community organisation and cell variety distribution,” Associate Professor Chuang reported.
“These results have sizeable implications for how brain framework styles operate, and how to forecast exercise dependent on the expertise of this composition. Additional nearly, what we now know will affect the structure of DBS and other brain stimulation methods.
“The next measures are to operate with clinicians versed in mind stimulation to decide how we can utilise this understanding put together with human data to support increase our knowledge of DBS.”
This additional thorough knowledge could help us to improved predict DBS effects and possibly strengthen its design and style for much better therapeutic results.
About this neurotech and DBS investigation news
Author: Merrett Pye
Source: College of Queensland
Get in touch with: Merrett Pye – College of Queensland
Impression: The image is credited to Associate Professor Kai-Hsiang Chuang / Queensland Mind Institute
Authentic Exploration: Closed entry.
“Hemodynamic transient and functional connectivity observe structural connectivity and cell kind about the brain hierarchy” by Kai-Hsiang Chuang. PNAS
See also

Summary
Hemodynamic transient and functional connectivity comply with structural connectivity and mobile sort around the brain hierarchy
The neural circuit of the brain is structured as a hierarchy of functional models with extensive-ranging connections that aid information and facts stream and useful connectivity. Studies utilizing MRI point out a average coupling concerning structural and useful connectivity at the process degree.
On the other hand, how do connections of diverse instructions (feedforward and comments) and locations with distinctive excitatory and inhibitory (E/I) neurons form the hemodynamic activity and functional connectivity above the hierarchy are unfamiliar.
Right here, we utilized purposeful MRI to detect optogenetic-evoked and resting-condition activities above a somatosensory pathway in the mouse mind in relation to axonal projection and E/I distribution.
Utilizing a very delicate ultrafast imaging, we identified comprehensive activation in areas up to the 3rd get of axonal projections pursuing optogenetic excitation of the ventral posteriomedial nucleus of the thalamus.
The evoked response and useful connectivity correlated with feedforward projections far more than suggestions projections and weakened with the hierarchy.
The hemodynamic reaction exhibited regional and hierarchical distinctions, with slower and a lot more variable responses in higher-order areas and bipolar response predominantly in the contralateral cortex.
Electrophysiological recordings recommend that these replicate discrepancies in neural exercise rather than neurovascular coupling. Importantly, the constructive and adverse parts of the hemodynamic response correlated with E/I neuronal densities, respectively. Moreover, resting-point out functional connectivity was additional related with E/I distribution, whereas stimulus-evoked helpful connectivity followed structural wiring.
These findings indicate that the structure–function partnership is projection-, mobile-sort- and hierarchy-dependent. Hemodynamic transients could reflect E/I activity and the elevated complexity of hierarchical processing.
